What is the endomembrane system and its function?
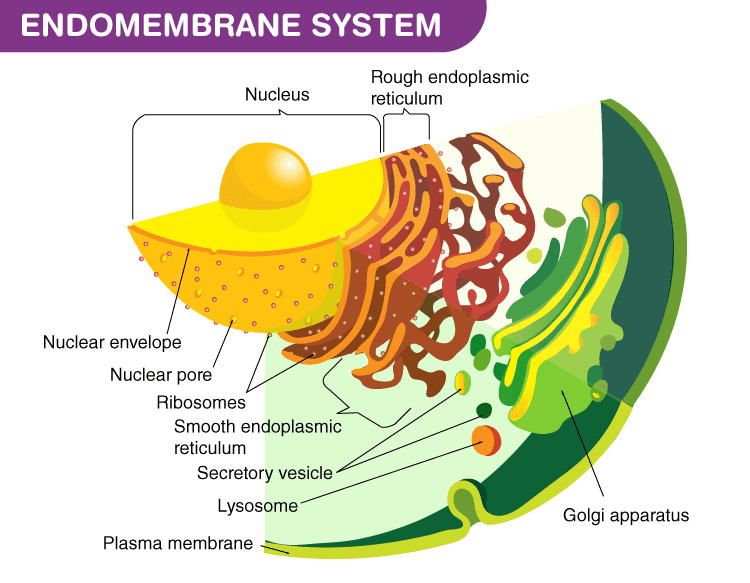
- The endomembrane system is a network of membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells.
- It includes various cellular structures, such as the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vesicles, and nuclear envelope.
- The primary function of the endomembrane system is to coordinate the transport, modification, and breakdown of proteins and lipids within the cell.
- The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) plays a significant role in the synthesis of proteins and lipids. It can be divided into the rough ER (RER), which has ribosomes attached to its surface, and the smooth ER (SER), which lacks ribosomes.
- The RER is involved in the production of proteins, while the SER is responsible for lipid synthesis, detoxification, and calcium ion storage.
- After synthesis, proteins are transported from the ER to the Golgi apparatus via vesicles. The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages these proteins for transportation to their final destination, either within or outside the cell.
- Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles involved in the breakdown of cellular waste, recycling of components, and digestion of foreign materials.
- Vesicles are small, membrane-bound sacs that transport molecules within the endomembrane system, as well as to and from the cell membrane.
- The nuclear envelope, consisting of two membranes, encloses the nucleus and controls the movement of materials between the nucleus and the rest of the cell.
- The endomembrane system plays a critical role in maintaining cellular homeostasis, regulating molecular traffic, and ensuring proper cellular function.
What are the four organelles in endomembrane system?
The four major organelles within the endomembrane system are:
1. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER):
This organelle consists of a network of membranous tubules and sacs and can be divided into two types: rough ER (RER) and smooth ER (SER). The RER has ribosomes attached to its surface and is involved in protein synthesis, while the SER lacks ribosomes and performs functions such as lipid synthesis, detoxification, and calcium ion storage.
2. Golgi apparatus:
It is composed of membrane-bound stacks of flattened sacs called cisternae. The Golgi apparatus receives proteins and lipids from the ER and modifies, sorts, and packages them for distribution to their final destinations. It is also involved in the synthesis of certain complex carbohydrates.
3. Lysosomes:
These organelles contain digestive enzymes enclosed within a single membrane. Lysosomes play a crucial role in intracellular digestion, breaking down various materials such as worn-out organelles, cellular debris, and foreign substances that enter the cell.
4. Vesicles:
Vesicles are small, spherical, membrane-bound sacs that transport molecules within the endomembrane system, as well as to and from the cell membrane. They are responsible for the movement of proteins, lipids, and other cellular materials between different compartments of the endomembrane system and to the cell surface.
These four organelles work together to ensure the proper synthesis, modification, sorting, and transport of proteins, lipids, and other molecules within the cell, contributing to cellular function and homeostasis.
Which organelles are NOT the part of the endomembrane system and why?
The organelles that are not part of the endomembrane system include:
1. Mitochondria:
- Mitochondria are double-membrane-bound organelles, often referred to as the "powerhouses" of the cell.
- They are responsible for carrying out cellular respiration and generating energy in the form of ATP.
- Mitochondria have their own DNA and replicate independently of the cell's nucleus.
- While mitochondria are involved in energy production and cellular metabolism, they are not directly connected to the endomembrane system as they have their own distinct structure and function.
2. Peroxisomes:
- Peroxisomes are small, single-membrane-bound organelles that contain enzymes involved in various metabolic reactions.
- They play a crucial role in processes such as lipid metabolism, detoxification of harmful substances, and the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide.
- Peroxisomes are not part of the endomembrane system because they are not connected to the ER, Golgi apparatus, or other organelles within that system.
- They have a separate origin and structure.
These organelles have specific functions that are unique to them and are not directly involved in the synthesis, modification, sorting, or transport of proteins or lipids within the endomembrane system. Instead, mitochondria and peroxisomes have specialized roles related to energy production, metabolism, and detoxification within the cell.