➥ Nucleus: discovered by Robert Brown in 1831
➥ Mitochondria: discovered by Carl Benda in 1898
➥ Chloroplasts: discovered by Julius von Sachs in 1866
➥ Endoplasmic Reticulum: discovered by Keith Porter in 1945
➥ Golgi Apparatus: discovered by Camillo Golgi in 1898
➥ Lysosomes: discovered by Christian de Duve in 1955
➥ Ribosomes: discovered by George Palade in 1955
➥ Peroxisomes: discovered by Christian de Duve in 1965
➥ Centrosomes: discovered by Theodor Boveri in 1888
➥ Cytoplasmic Membranes: discovered by Albert Claude in 1945
➥ Vacuoles: discovered by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1676
➥ Cell Membrane: discovered by Hugh Davson and James Danielli in 1935
➥ Nucleolus: discovered by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1682
➥ Nucleolar Membrane: discovered by Karl Wilhelm Zimmermann in 1783
➥ Cytoplasms: discovered by Rudolf Virchow in 1855
➥ Microvilli: discovered by James F. Danielli and Hugh Davson in 1935
➥ Flagella: discovered by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1676
➥ Cilia: discovered by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1676
➥ Microtubules: discovered by Keith Porter in 1949
➥ Intermediate Filaments: discovered by Keith Porter in 1953
➥ Microfilaments: discovered by Evelyn Witkin in 1947
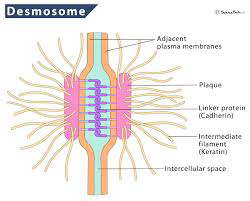
➥ Desmosomes: discovered by Jean-Pierre Bourgin and André Boivin in 1956
Desmosomes are adhesive intercellular junctions that mechanically integrate adjacent cells by coupling adhesive interactions mediated by desmosomal cadherins to the intermediate filament cytoskeletal network.
➥ Tight Junctions: discovered by Franz Schmid in 1899
➥ Gap Junctions: discovered by J. F. A. P. Miller and J. C. van der Noen in 1967
➥ Nucleoloid: discovered by Emil Godlewski in 1880